Different types of vaccines as well as their role
What is a vaccine?
The vaccine is a biological prep using a fundamental prophylactic purpose: it contains an agent (bacterium, virus or poison) whose introduction to the bloodstream of the human body aids APC cells, T cells and B cells to accommodate to the new pathogen and also to create a new pathogen. -effective response in dealing with it.
How can the vaccine assist?
Vaccines prevent the development of infectious diseases because of this so-called. “Collective immunity”. The latter means that a decent proportion of the populace ought to be immunized against infectious illness in order to decrease the danger of spread. By boosting the protective influence,”collective immunity” favors organisms that may not be vaccinated because of weak immune systems, chronic allergies or diseases.
Vaccine history
Though Edward Jenner is usually considered the inventor of the initial vaccine in 1796, its own history is in fact much older. Chinese intentionally infected individuals using smallpox (by inhalation of this Pathogen through the nose by scraping the substance on skin) in 1000 BC. The goal was to decrease the impact of this disease and create resistance Against potential infections.
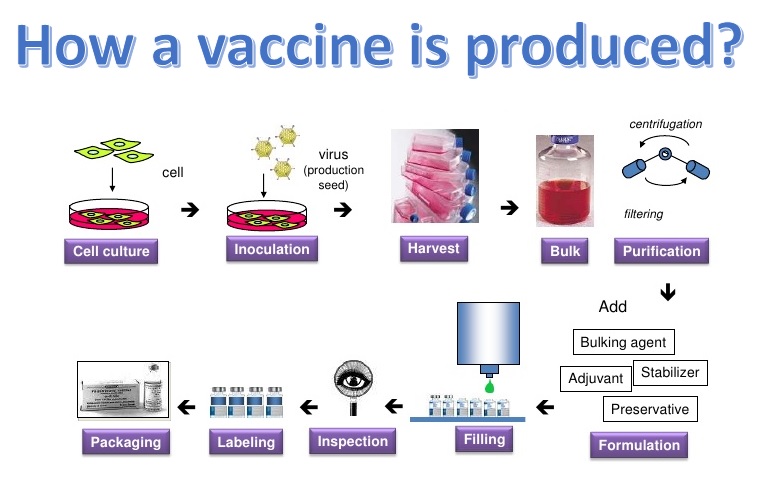
Types of vaccines
There are currently five major types of vaccines.
Live, attenuated vaccines contain a weakened version of the infectious agent. Viruses usually attenuate following being increased for quite a while in irregular cells. Once adapted to the new environment, viruses are unable to replicate effectively in the individual host, since they might otherwise. All these are the following vaccines:
- Against smallpox;
- Against measles, mumps and rubella;
- Against chickenpox;
- Against influenza;
- Against rotavirus;
- Sharp;
- Against yellow fever;
Inactivated vaccines
Inactivated vaccines contain a killed (by the use of chemicals, radiation or heating) version of the infectious agent. Yeah, they’re like that:
- Inactivated polio vaccine;
- Against hepatitis A;
- Against influenza;
- Against rabies;
- Against bubonic plague;
- Against cholera.
Toxoid vaccines
Toxoid vaccines prevent diseases caused by bacteria that produce toxins in the body. These types of vaccines contain an inactivated version of a toxin called a toxoid whose antigenic properties are maintained:
- Against tetanus;
- Against diphtheria;
- Against whooping cough.
Subunit vaccines
Subunit vaccines Comprise only the Significant antigens of the agent causing the Illness: they Might Comprise from 1 to 20 antigens Obtained directly from the virus or Increased in a Lab:
- Against hepatitis B;
- Against human papillomavirus.
Conjugated vaccines
Conjugated vaccines contain polysaccharides, normally the surface layer of bacteria, related to protein carriers. If the bacteria enter the body, then the antibodies will recognize their sugar level and restrict the bacteria from causing illness:
- Against Haemophilus influenzae type B;
- Pneumococcal vaccine;
- Meningococcal vaccine.
When there will be a vaccine for COVID-2019?
Since 2003 the Entire World has Confronted three outbreaks caused by coronaviruses: Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS), and now the current outbreak caused by a virus known as 2019-nCoV.
Due to Researchers have yet to Locate a way to Prevent these outbreaks before they begin. But within the past 17 decades, they’ve radically shortened the time necessary to create a vaccine following a new virus emerges.
This is largely because of technological improvements and a higher commitment by governments and nonprofits to funding research on emerging infectious diseases. Researchers are already rushing to develop a Vaccine for 2019-nCoV — a feat that specialists say is possible, But still might not arrive in time to aid in this outbreak.
