Comprehensive genetic testing identifies targetable genomic alterations in most patients with non-small cell lung cancer, specifically adenocarcinoma, single institute investigation.
This examine critiques intensive genetic evaluation in superior non-small cell lung most cancers (NSCLC) patients in order to: describe how targetable mutation genes interrelate with the genes recognized as variants of unknown significance; assess the share of patients with a doubtlessly targetable genetic alterations; consider the share of patients who had concurrent alterations, beforehand thought of to be mutually unique; and characterize the molecular subset of KRAS.
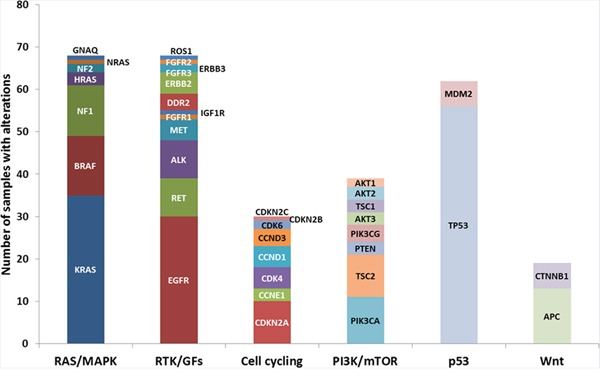
Thoracic Oncology Research Program Databases on the University of Chicago supplied affected person demographics, pathology, and outcomes of genetic testing. 364 patients together with 289 adenocarcinoma underwent genotype testing by numerous platforms similar to FoundationOne, Caris Molecular Intelligence, and Response Genetics Inc.
For the whole adenocarcinoma cohort, 25% of patients had been African Americans; 90% of KRAS mutations had been detected in people who smoke, together with present and former people who smoke; 46% of EGFR and 61% of ALK alterations had been detected in by no means people who smoke.
99.4% of patients, whose samples had been analyzed by next-generation sequencing (NGS), had genetic alterations recognized with a median of 10.8 alterations/tumor all through totally different tumor subtypes.
However, mutations weren’t mutually unique. NGS in this examine recognized doubtlessly targetable genetic alterations in the vast majority of patients examined, detected concurrent alterations and supplied info on variants of unknown significance at the moment however doubtlessly targetable in the long run.
Genotyping serotonin transporter polymorphisms 5-HTTLPR and rs25531 in European- and African-American topics from the National Institute of Mental Health’s Collaborative Center for Genomic Studies.
A variety of research have advised DNA sequence variability in the serotonin transporter gene (SLC6A4) between European-American (EA) and African-American (AA) populations, which may very well be clinically vital, given the central position SLC6A4 has in serotonin transmission.
However, these research have had comparatively small samples, used self-reported measures of race, and have solely examined the promoter-linked polymorphism 5-HTTLPR. Here we genotype 5-HTTLPR and rs25531, a neighboring useful polymorphism, in 954 AA and 2622EA topics from a National Institute of Mental Health repository pattern.
Genotyping was carried out utilizing fragment evaluation by capillary electrophoresis. AA, as in contrast with EA, teams had decrease frequencies of the S allele (0.25 vs 0.43) and SS genotype (0.06 vs 0.19) at 5-HTTLPR, and better charges of the G allele at rs25531 (0.21 vs 0.075). A uncommon xL variant at 5-HTTLPR was additionally extra widespread amongst AAs (0.017 vs 0.008).
When the polymorphisms had been redefined right into a high- and low-transcription haplotypes, the AA group confirmed considerably fewer low-transcription variants (χ(2)=4.8, P=0.03).
No genotypes had been related with main melancholy, any nervousness dysfunction, or neuroticism in both EA or AA populations. This is the most important examine to indicate SLC6A4 genotype variations between EA and AA populations, and the primary to incorporate rs25531. Lack of associations with scientific outcomes could replicate untested moderating environmental influences.
